Industrial Heritage
Rehabilitation of the Former Pottery complex Santa Ana as the Pottery centre of Triana

Rehabilitation of the Former Pottery complex Santa Ana as the Pottery centre of Triana Author: AF6 ARCHITECTURE Image of the courtyard. Author: Jesus Granada. 2013
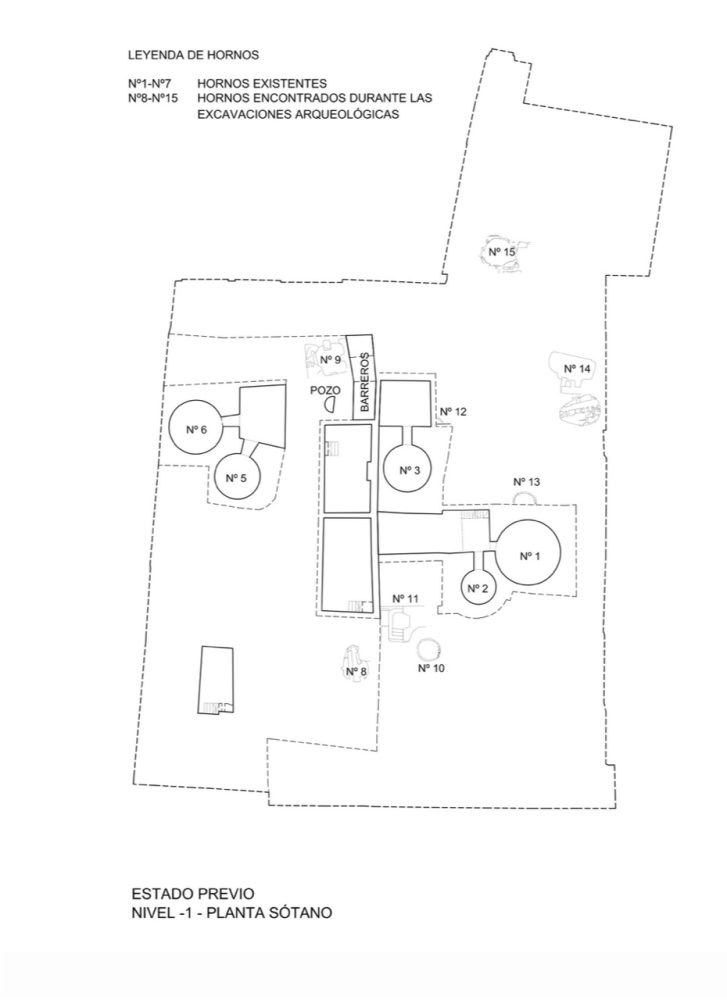
Rehabilitation of the Former Pottery complex Santa Ana as the Pottery centre of Triana Author: AF6 ARCHITECTURE Previous state and archaeological excavations. Author: AF6 Arquitectura
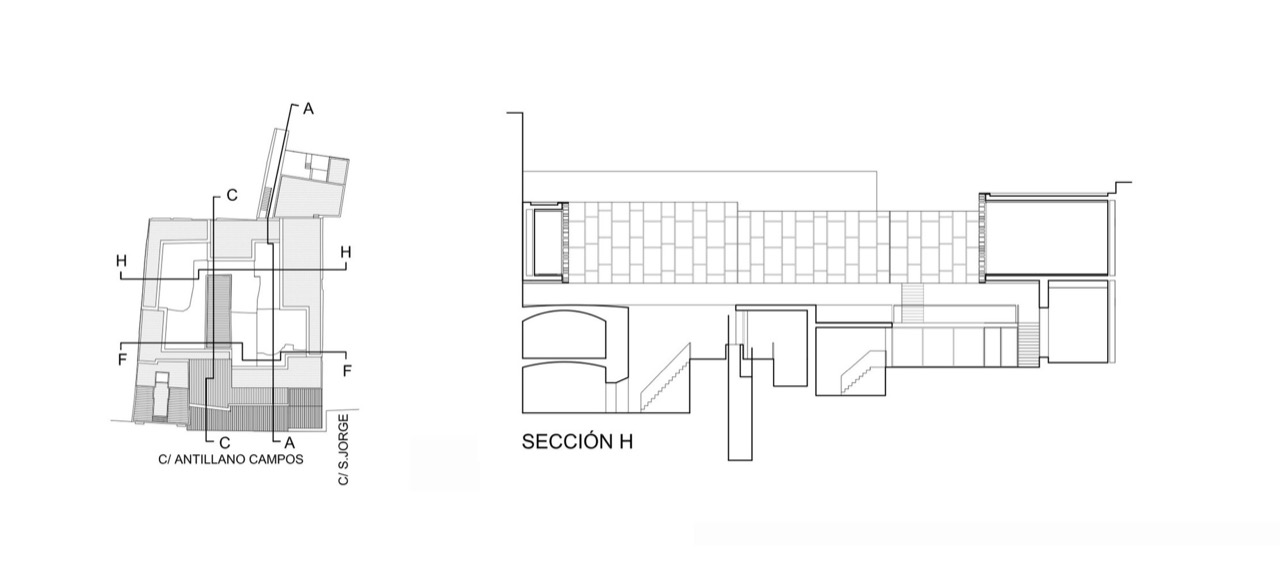
Rehabilitation of the Former Pottery complex Santa Ana as the Pottery centre of Triana Author: AF6 ARCHITECTURE Section and plan after the reconstruction. Author: AF6 Arquitectura

Rehabilitation of the Former Pottery complex Santa Ana as the Pottery centre of Triana Author: AF6 ARCHITECTURE Exterior image of the access. Author: Jesus Granada. 2013

Rehabilitation of the Former Pottery complex Santa Ana as the Pottery centre of Triana Author: AF6 ARCHITECTURE Organisation of the different volumes that make up the ensemble. Author: Jesus Granada. 2013
As a starting point, we assume the definition of Industrial Heritage as that established by the National Plan for Industrial Heritage: By industrial heritage we understand the suite of movable and immovable assets and sociability systems associated with the working culture generated by the extraction, transformation, transport, distribution and management activities of the economic system that emerged from the industrial revolution. These assets have to be understood as an integral whole comprised of the landscape in which they stand, the industrial relations that structures them, the architectures that characterise them, the techniques used in their procedures, the archives generated during their activity and their symbolic practices.
In the 21st century we are confronted by new challenges with respect to research, protection and the activation of heritage. The ever-stronger bonds between natural heritage and cultural heritage, between movable and immovable heritage, between tangible and intangible heritage, between object and context, between specialized technical management and citizen participation, between rural and urban, between local and urban, between local and global, between singular and generic, between concentrated and dispersed, all makes us think that we find ourselves before a new patrimonial border.